Restricted Earth Fault Protection – Application and Guidelines

Restricted Earth Fault (REF) protection is an essential safeguard measure that protects electrical systems against earth faults, especially for high-value apparatuses, including transformers, generators, and alternators. This protection method is particularly aimed at identifying low-magnitude faults in a specific region and thereby responds appropriately to reduce impact within this region. Explore why REF protection is essential, how it operates, and where it is commonly applied.
Table of Contents
- What is Restricted Earth Fault Protection?
- Why Restricted Earth Fault Protection is Needed?
- Difference Between Earth Fault and Restricted Earth Fault Protection
- Restricted Earth Fault Protection Working Principle
- Application of Earth Fault Protection
- Advantages of Restricted Earth Fault Protection
- Challenges in Implementing Restricted Earth Fault Protection
- Restricted Earth Fault Protection of Generator
- Restricted Earth Fault Protection of Alternator
- Restricted Earth Fault Protection Calculation
- How does Restricted Earth Fault Protection Work?
- Why Lauritz Knudsen Electrical and Automation for REF Protection?
- Conclusion
- FAQ
What is Restricted Earth Fault Protection?
Restricted earth fault protection is a special type of earth fault protection designed for a particular region called a Restricted Zone. While general earth fault protection may pick faults at any point in an electrical system, REF protection has a degree of selectivity because it functions only at the specific zone assigned. This selective feature makes REF protection very valuable for most important applications, such as transformers and generators, for which it may be important to locate and isolate a fault in a matter of a few cycles to avoid significant damage.
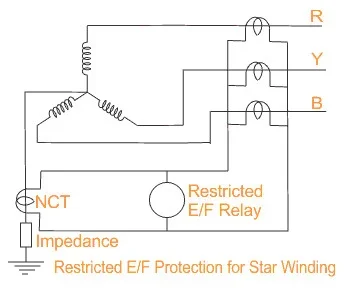
Why Restricted Earth Fault Protection is Needed?
Restricted earth fault protection is crucial for modern power systems. It is especially important where precision fault detection is essential. REF identifies even minor faults localized to specific zones. It safeguards assets like alternators and transformers by offering faster fault clearance, minimizing risks of damage, outages, and costly maintenance.
1. Limited Sensitivity of Conventional Earth Fault Protection
Standard earth fault protection devices cover wide zones. They may not detect small internal faults in generator windings. This lack of sensitivity can cause undetected damage. REF overcomes this by providing localized protection with higher precision. This offers early fault detection before issues escalate into severe equipment failures or outages.
2. Critical Equipment Needs Higher Protection Precision
Generators and transformers are high-value assets that operate under continuous load. The restricted earth fault protection of the generator ensures specific monitoring of stator windings. This enables swift isolation of faults. It helps prevent insulation breakdowns and improves the operational safety and lifespan of such mission-critical equipment.
3. Reduces Downtime and Repair Costs
By using a restricted earth fault relay, faults are detected and isolated faster. This reduces the extent of damage. It minimizes maintenance efforts and prevents long shutdowns. REF protection ensures higher uptime and protects against unexpected repair costs due to unmonitored internal faults.
4. Improved Selectivity and Zone-Based Protection
The difference between earth fault and restricted earth fault lies in zone selectivity. While earth fault systems act broadly, REF focuses on specific sections. This limits unnecessary system tripping and improves protection granularity. It ensures only the affected zone is isolated, leaving the rest of the system fully operational.
Difference Between Earth Fault and Restricted Earth Fault Protection
The distinguishing factor between standard earth fault and restricted earth fault protection is the area of operation and selectiveness. Standard earth fault protection is available for the whole system and possesses relatively low selectivity. This sort of arrangement might not be applicable in identifying faults that may occur in certain regions since the protection may not be activated due to low fault currents. On the other hand, restricted earth fault protection operates only in a particular zone of the system or from one phase to another, such as from the transformer winding of the generator stator. It provides higher sensitivity to this limited area and reduces the risks of experiencing a fault blowing up the whole system when it has been detected and undone individually.
| Feature | Earth Fault Protection | Restricted Earth Fault Protection |
|---|---|---|
| Protection Zone | Provides protection for the entire electrical system or a wide area. | Protects a specific zone, such as generator stator or transformer winding. |
| Sensitivity | Generally less sensitive, may miss low-magnitude internal faults. | Highly sensitive, detects even minor faults in defined zones. |
| Selectivity | Low selectivity—may trip for faults outside the core fault zone. | High selectivity, trips only when a fault occurs within the protected area. |
| Application Areas | Used in general systems and lower-critical areas. | Commonly used for generators, alternators, and transformers. |
| Relay Type | Uses a standard earth fault relay. | Uses a specialized restricted earth fault relay. |
| Current Transformer Requirement | May need a single CT for phase or neutral. | Requires multiple CTs (typically on neutral and phase) for differential current measurement. |
| Cost & Complexity | Lower cost, simpler setup. | Slightly higher cost, but offers better fault accuracy and reliability. |
Restricted Earth Fault Protection Working Principle
Restricted earth fault protection is based on the differential current principle, which identifies faults within a defined zone by detecting imbalances in current. This principle is highly effective in isolating faults in sensitive equipment like generators and alternators, using a restricted earth fault relay to ensure fast and accurate response.
1. Differential Current Detection
The core of the restricted earth fault relay working principle lies in differential current detection. When the incoming and outgoing currents of a protected zone differ, it indicates a fault. The REF relay responds to this imbalance instantly. It isolates the faulted section while keeping the rest of the system operational.
2. Use of Multiple Current Transformers
Restricted earth fault protection of the generator typically involves multiple current transformers (CTs) installed at both ends of the winding. These CTs continuously monitor current flow. When an earth fault occurs within the protected zone, the CTs sense the imbalance. This prompts the REF relay to act swiftly and precisely.
3. Zone-Based Fault Sensitivity
One of the major benefits of restricted earth fault protection is its zone-based design. Unlike conventional earth fault protection, which may respond to any fault, REF targets only a specific area, such as a generator stator. This high sensitivity prevents system-wide shutdowns due to small, localized faults.
4. Fast Isolation and Trip Command
Upon fault detection, the restricted earth fault relay issues a trip signal to the circuit breaker. This immediate action helps prevent insulation damage or winding failure. The relay’s fast operation is crucial for high-stress equipment. This ensures protection without delay and avoiding unnecessary downtimes or expensive repairs.
Application of Earth Fault Protection
Restricted earth fault protection is widely used in several applications, particularly in scenarios requiring precise fault isolation:
- Transformers: Various types of REF protection are used in transformers mainly for protection of the winding in the case of internal fault. Restricting the fault detection zone to the transformer windings means that REF relays can detect the slightest faults, therefore controlling the damage that can occur.
- Generators and Alternators: REF protection for generators and alternators is necessary as frequent insulation failures characterise these elements. This protection scheme ensures early detection; thus, there is usually little damage when an accident occurs.
- Motors: In large motors, it is possible to apply REF protection to prevent the flow of faults and affect connected equipment.
- Busbars: Fault detection within busbars may be implemented using REF protection to obtain very accurate detection of faults, which is necessary for the system's proper functioning.
Advantages of Restricted Earth Fault Protection
Restricted earth fault protection is critical for safeguarding specific zones like transformer windings or stator areas in generators. It detects even low-magnitude faults with high accuracy. The device minimizes damage and system disruption by isolating the affected zone quickly. This makes it ideal for sensitive electrical equipment protection.
1. Enhanced Sensitivity for Localized Faults
The restricted earth fault protection of generators and alternators provides extremely high sensitivity. It ensures even the smallest faults are identified early. This reduces risks. The feature is crucial for areas where standard earth fault protection fails due to low fault currents. These include winding faults in large electrical machines.
2. Fast and Accurate Tripping Mechanism
The restricted earth fault protection relay acts instantly by detecting imbalance in currents. This ensures minimal equipment damage and swift isolation of faults. The speed of operation, especially in high-value equipment like transformers and alternators, helps prevent escalation. This ensures smoother and safer power distribution.
3. Zone-Based Protection Increases System Reliability
REF protection operates within defined boundaries of a system, such as stator windings or transformer zones. This difference between earth fault and restricted earth fault improves system reliability by reducing unnecessary tripping. It enhances selectivity. Also, it ensures that only the faulted section is isolated without impacting the broader network.
4. Reduced Maintenance and Downtime Costs
With restricted earth fault relay working principle based on precise differential protection, fault detection is quick and accurate. This early intervention prevents major system failures. It leads to reduced repair costs. This also ensures lower equipment wear and tear. Hence, it minimizes operational downtime and extends asset life.
Challenges in Implementing Restricted Earth Fault Protection
Restricted earth fault protection offers significant benefits. However, its implementation can be technically demanding. Challenges include proper relay selection, CT alignment, and system calibration. These factors, if not properly managed, can affect detection accuracy and cause misoperations. This is especially in complex generator and transformer applications.
1. Complex Relay Settings and Calibration
Set up of a restricted earth fault protection relay requires careful calculation and precise calibration. Incorrect settings may lead to nuisance tripping or failure to detect genuine faults. Accurate restricted earth fault protection calculation is crucial for ensuring the system functions as intended. This is especially important in sensitive industrial environments.
2. High Initial Implementation Cost
Though it reduces long-term damage, implementing REF protection comes with a higher upfront cost. Specialized earth fault protection devices, CTs, and intelligent relays like restricted earth fault relay increase initial investment. This makes it less appealing for budget-constrained installations despite long-term benefits.
3. Current Transformer Matching Issues
The effectiveness of restricted earth fault protection of alternators depends heavily on perfectly matched current transformers. Any mismatch can cause errors in fault detection or false tripping. CT alignment is critical and must be maintained precisely to ensure proper performance of the REF protection system.
4. Limited Protection Zone Coverage
One of the main limitations is that restricted earth fault protection only safeguards specific areas. It doesn’t provide protection for the entire electrical system. Therefore, it must be used in conjunction with broader earth fault protection to ensure comprehensive safety and system reliability.
Restricted Earth Fault Protection of Generator
Restricted earth fault protection of generator is crucial for detecting internal insulation failures in stator windings. It operates within a defined protection zone, offering faster, more sensitive fault identification than standard protection methods. This improves reliability, prevents major breakdowns, and enhances safety in continuous power generation environments.
1. Protection of Stator Windings
The stator windings in generators are prone to earth faults due to insulation wear. REF protection accurately detects and isolates these faults. It prevents severe internal damage and avoids operational interruptions. This ensures safer functioning, especially in industrial setups running high-voltage generator systems.
2. Use of Differential Current Method
This method monitors the difference between incoming and outgoing current through CTs. If a mismatch is detected, the REF system considers it a fault. This ensures the protection remains restricted to the generator's stator, offering precise and localized fault detection.
3. Fast Tripping Mechanism
Speed is essential in fault handling. The REF system initiates instant tripping when a fault is detected, typically within milliseconds. This rapid response minimizes equipment damage, lowers repair costs, and avoids cascading effects throughout the power network.
4. Enhanced Sensitivity and Zone Protection
REF protection provides high sensitivity in a narrow protection zone, such as the stator. Unlike traditional earth fault protection devices, this focused coverage allows for detection of even low-magnitude faults. It ensures no issue goes undetected or unresolved in critical equipment.
Restricted Earth Fault Protection of Alternator
Restricted earth fault protection of alternator ensures precise monitoring and detection of internal winding faults. Alternators operate under high electrical stress, and REF protection safeguards their windings from insulation failure and fault propagation. It helps maintain efficiency, uptime, and safety across modern power systems.
1. Fault Detection in Alternator Windings
Alternator windings, if left unprotected, may suffer catastrophic damage due to internal faults. REF protection ensures these faults are caught early through sensitive CT-based monitoring systems, allowing operators to respond promptly and avoid downtime.
2. Use of Restricted Earth Fault Relay
The restricted earth fault relay is key in detecting even slight imbalances in current, which indicate internal earth faults. Its reliable operation helps preserve alternator health and ensures accurate, localized protection without interfering with the rest of the system.
3. Selective Zone Isolation
REF protection isolates faults specifically in the alternator’s winding zone. This prevents unnecessary tripping of unrelated equipment and maintains system stability. Selective isolation also reduces the complexity of troubleshooting and accelerates recovery time.
4. Synchronization with Protection Systems
When integrated with other protection devices, REF protection enhances alternator safety. It works in sync with overcurrent and thermal relays to offer a comprehensive safety net, which is especially important in mission-critical power generation environments.
Restricted Earth Fault Protection Calculation
The settings for restricted earth fault protection can be calculated, although the threshold level required to detect a fault without tripping must be defined first. The calculations are based on the following factors:
- Primary Current: The current that flows through the equipment exposed to the protection risk by the mentioned zone.
- Fault Level: The rated or minimum fault current that the relay has to detect to minimise the chances of a false trip and ensure it can detect the highest possible value of fault current.
- CT Ratios: The transformer ratios determined in the contemporary vary depending on the equipment rating for an accurate measurement.
How Does Restricted Earth Fault Protection Work?
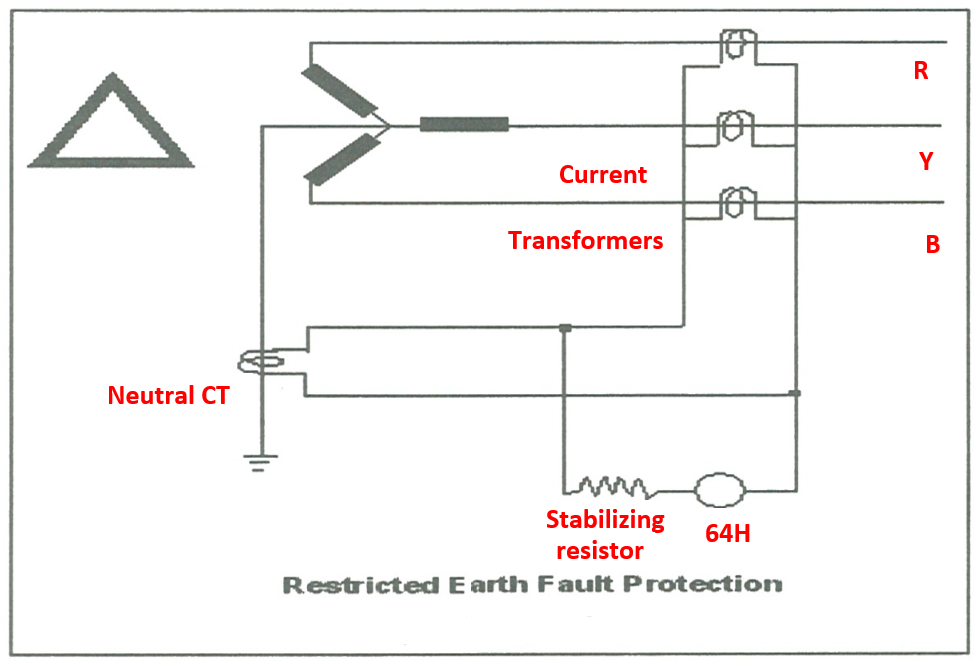
Restricted earth fault protection works by monitoring current at both ends of a defined electrical zone, such as a generator or alternator winding, using current transformers (CTs). When a fault occurs within this zone, the resulting current imbalance triggers the restricted earth fault relay. This isolates the fault through a trip signal.
1. Role of Current Transformers
Multiple CTs are installed at the input and output terminals of the protected zone. These devices measure the current flow continuously. Any imbalance between incoming and outgoing current, caused by an earth fault, is immediately detected by the CTs. This enables the restricted earth fault protection system to respond effectively.
2. Relay Activation Process
When current imbalance is detected, the restricted earth fault relay activates. Based on its working principle, it processes the differential current and sends a trip command to disconnect the faulty section. This ensures targeted isolation, avoiding system-wide outages and minimizing damage to the protected equipment.
3. Trip Command to Breaker
Upon detecting a fault, the REF relay signals the circuit breaker to operate. This quick disconnection protects components like alternators and transformers from thermal and mechanical damage. The restricted earth fault protection of alternator is especially vital due to the high value and critical nature of such assets.
4. High Sensitivity and Reliability
Restricted earth fault protection provides a much more sensitive and reliable response than standard earth fault systems. Even low-magnitude faults, which might go undetected otherwise, are isolated effectively. This protects both equipment lifespan and operational uptime in critical power systems.
Why Lauritz Knudsen Electrical and Automation for REF Protection?
Lauritz Knudsen specialises in electrical protective equipment, providing the latest restricted earth fault protection. Our systems offer the best-guaranteed shield for vital assets like transformers, generators, and alternators. Having several years of professional experience in electrical and automation technology, Lauritz Knudsen guarantees that all protection systems are designed and function optimally for detecting earth faults.
Also Read: Everything You Need to Know About EARTH LEAKAGE CIRCUIT BREAKER (ELCB)
Conclusion
Restricted Earth Fault (REF) protection is an infrequent but efficient solution for protecting sensitive electrical equipment against earth faults. This is important where accuracy and speed are important, as in transformers, generators, and alternators, since it isolates faults within a restricted area. Thus, the principles, application, and basic calculation of REF protection allow engineers to reduce the risk and cost of problems appearing in systems. Lauritz Knudsen Electrical and Automation provides best-in-class REF protection solutions with an emphasis on the safety of all electronics and steady functionality of the concerned system, thus making it ideal for industries seeking better protection for their electrical systems.
FAQ
Q1. How does REF protection differ from conventional earth fault protection?
Ans: Restricted Earth Fault (REF) protection is zone-specific and offers higher sensitivity than conventional earth fault protection. REF protection isolates faults within defined zones like stator windings. This provides faster, more accurate fault detection and minimizes system-wide impact.
Q2. Which equipment requires REF protection?
Ans: REF protection is essential for high-value equipment such as generators, alternators, and power transformers. These components are prone to internal winding faults, and REF relays provide localized, sensitive protection to prevent costly damage and prolonged downtime. It is particularly important in power plants and industrial electrical networks.
Q3. What type of relay is used in REF protection?
Ans: Restricted Earth Fault protection typically uses high-impedance differential relays or numerical REF relays. These relays measure the difference in current entering and exiting a protected zone. A significant imbalance indicates a fault. It triggers the relay to isolate the fault quickly. This ensures reliable operation of critical power systems.
Q4. Can REF protection operate for phase-to-phase faults?
Ans: REF protection is designed exclusively to detect earth faults within a defined area, such as transformer or generator windings. It cannot detect phase-to-phase faults. This requires separate protection schemes like differential or overcurrent protection to ensure complete system reliability and safety.
Q5. What is the typical response time of an REF relay?
Ans: The response time of a restricted earth fault relay is extremely fast. It is typically in the range of 20 to 40 milliseconds. This rapid action ensures minimal damage to equipment and supports seamless operation in critical infrastructure. This makes REF relays essential for sensitive and high-priority systems.
Q6. What are the advantages of high-impedance REF protection?
Ans: High-impedance REF protection offers excellent stability, sensitivity, and selectivity. It prevents nuisance tripping. This ensures that only genuine faults cause activation, and works effectively even in systems with multiple CTs. It is widely used in generator and transformer REF schemes for precise fault detection.
Q7. How often should REF relays be tested?
Ans: REF relays should ideally be tested during annual maintenance schedules or after any system fault. Regular testing ensures relay accuracy, verifies CT integrity, and confirms correct wiring. Preventive testing improves system reliability and ensures that restricted earth fault protection functions correctly when needed most.

